Neurotransmitters & Their Impact
Neurotransmitters are the chemical messengers that our nervous system uses to relay information in between neurons.
The way different parts of the brain communicate as well as how it processes stimuli from the outside world, depend on the body’s ability to synthesize and process these neurotransmitters.
Optimal neurotransmitter balance is required to maintain proper health. Imbalances can cause the brain and the body to be over- or under-stimulated, producing neurological or psychological symptoms.
Can Imbalanced Neurotransmitter Levels Impact Health?
Like hormones, neurotransmitters require a delicate balance to keep the body functioning at a peak level.
Genetics, environment, chemicals and nutritional deficiencies are a few factors that can result in over- or under-production of neurotransmitters. Once out of balance, the nervous system begins to compensate – which, in time, can lead to neurological or psychological symptoms.
Some of the more common psychological conditions today are known to be accompanied by neurotransmitter imbalances. However, it’s also possible for individuals to present with similar symptoms yet have unique foundational imbalances. Testing helps clarify these root issues.
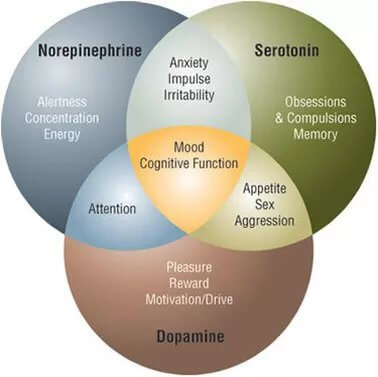
Excitatory Neurotransmitters:
Dopamine: generally regarded as the brain’s pleasure and reward center, plays the central role in addiction, improves attention, focus and motivation, and modulates movement control.
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine: regulate the “fight or flight” response, elevated blood pressure and heart rate, stimulate wakefulness and reduce digestive activity.
Glutamate: functions as the “on” switch in the brain. It’s the major excitatory neurotransmitter that decreases sleep, optimizes learning, memory and mood and improves libido.
Histamine: plays a role in the body as a neurotransmitter that increases metabolism, promotes wakefulness and suppresses appetite.
PEA (phenylethylamine): promotes energy, elevates mood, regulates attention, aggression and serves as a biomarker for ADHD.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters:
GABA: functions as the “off” switch in the brain. It’s the major inhibitory neurotransmitter that improves mood, relieves anxiety and promotes sleep.
Glycine: plays a dual role as a neurotransmitter and amino acid that serves as a building block to
proteins, improves sleep quality, calms aggression, and serves as an anti-inflammatory agent.
Serotonin: generally regarded as the “happiness molecule,” contributes to the feeling of calm and
well-being that eases depression and anxiety, supports sleep and decreases appetite.
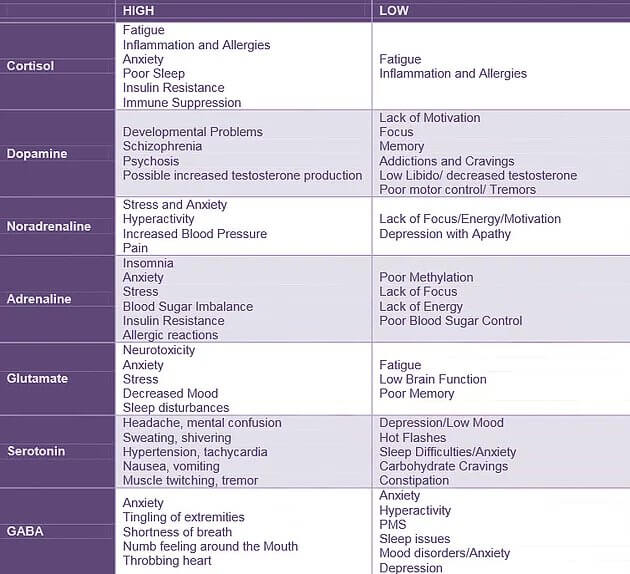
Neurotransmitter Imbalance & Chronic Conditions
Numerous neurotransmitter imbalances may cause persistent health concerns:
Anxiety & Depression: Imbalances are often associated with Glutamate (panic attacks), PEA, Histamine, Serotonin, as well as Epinephrine and Norepinephrine.
Fatigue: An imbalance between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters is likely.
Impulsivity: GABA, Dopamine and Serotonin are three chemical messengers commonly linked
to disorders like ADD, ADHD and OCD.
Insomnia: Glutamate, Histamine, Dopamine, GABA and Serotonin are several chemical messengers often linked to sleep disturbances and insomnia.
PMS or PMDD: Imbalances such as Serotonin, Dopamine, Norepinephrine and GABA are often involved.
Addictions and Cravings: Often associated with Dopamine and Serotonin deficiency
Case Study: Anxious Alisha
Alicia is a 32 year old pre-menopausal female with anxiety. Additionally she complains of morning fatigue, stress, sleep disturbances, headaches, sugar cravings, and increased urinary urge.
Below is her urinary neurotransmitter test results (ZRT Laboratory):
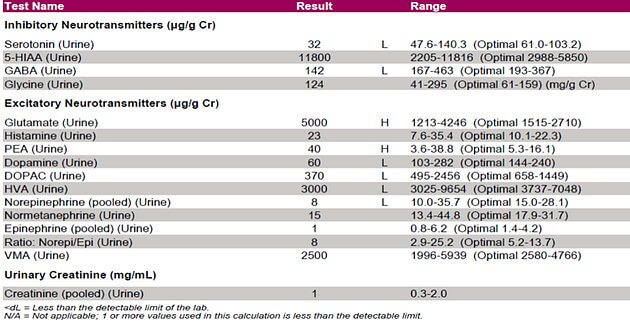
Alicia’s neurotransmitter profile shows the following issues:
1. Low levels of inhibitory neurotransmitters (Serotonin and GABA)
2. High levels of Glutamate
3. Low levels of Dopamine and Catecholamines
With the help of her Functional Medicine practitioner, Alicia then begins her treatment protocol, which involves lifestyle modification, nutritional modification, and nutraceutical supplementation to help balance her neurotransmitter levels.